The notion of permissions is crucial because it enables you to safely permit or deny access to the directory or files. Let's first examine permissions and how they operate. Three different permissions are available. : Read, Write, Do. Numbers are also used to denote permissions.
Read (4): The users who have been given this permission are able to read.
Write (2): The person who has the ability to write files or directories can do so.
Execute (1): The ability to execute files or directories is provided by the execute permissions.
Additional three categories of user groups are assigned the aforementioned permissions. World/Public, Group, and User.
Owner of the file or directory is this user.
Users who are members of the same organization.
Everyone who is not a user nor a member of any group is considered to be in the world/public.
To log in to the DirectAdmin control panel, please visit one of the following URLs:
- https://your-domain.com:2222
- https://IP-address:2222
- https://server-hostname:2222

Once logged in, navigate to the System Info & Files section and select File Manager.
In the File Manager, right-click on the directory you would like to modify and choose Set Permissions.
From there, you can either select the desired permissions or enter them in numerical format.
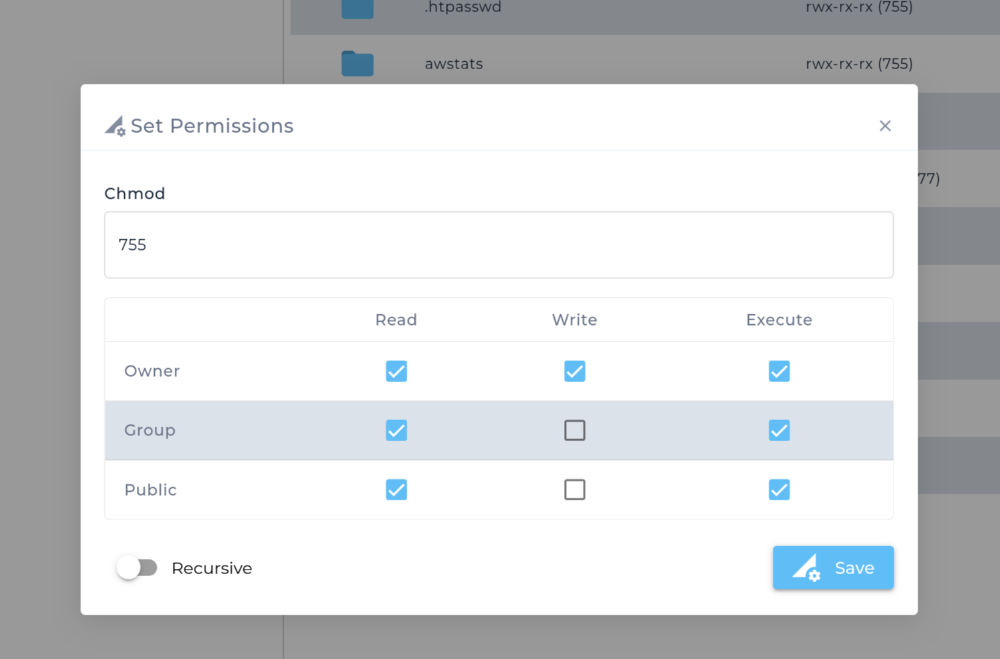
If you want to apply the new permissions to all files and directories within the selected directory, check the Recursive option.
Once you've made your changes, click on SAVE.
Congratulations! You have successfully changed the permission for the directory. This same method can be used to change the permissions of individual files as well.